Global CO 2 emissions were over 5% lower in Q1 than in Q1 19, mainly due to a 8% decline in emissions from coal, 45% from oil and 23% from natural gas CO 2 emissions fell more than energy demand, as the most carbonintensive fuels experienced the largest declines in demand during Q1This chart shows the change in global greenhouse gas emissions over time Greenhouse gases are measured in 'carbon dioxideequivalents' (CO 2 e) Today, we collectively emit around 50 billion tonnes of CO 2 e each year This is more than 40% higher than emissions in 1990, which were around 35 billion tonnesThe following program depicts the emissions of greenhouse gases by mass of "carbon equivalent" Data from the 07 IPCC report, 07 Climate Change 07 Synthesis Report Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Core Writing Team, Pachauri, RK and Reisinger, A
1
Global greenhouse gas emissions pie chart
Global greenhouse gas emissions pie chart-The pandemic will cause a dip in emissions, but this will only be temporary without a dramatic and planned shift to lowcarbon economies In 19, total greenhouse gas emissions, including landuse change, reached a new high of 591 gigatonnes of carbon dioxide equivalent (GtCO 2 e) This means that atmospheric concentrations of carbonGlobal emissions inventories for gases other than carbon dioxide are limited to fiveyear intervals The United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change database has more comprehensive data;




How To Neutralise Your Greenhouse Gas Footprint
This is a list of sovereign states and territories by carbon dioxide emissions due to certain forms of human activity, based on the EDGAR database created by European Commission and Netherlands Environmental Assessment Agency released in 18 The following table lists the 1990, 05 and 17 annual CO 2 emissions estimates (in Megatonnes of CO 2 per year) along with a list ofFigure ES2 is a pie chart displaying the breakdown of Canada's GHG emissions by six Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change sectors for 19 These sectors are the following Energy – Stationary Combustion Sources, Energy – Transport, Energy – Fugitive Sources, Industrial Processes and Product Use, Agriculture, and WasteThis pie chart sample shows the atmosphere air composition It was designed on the base of the Wikimedia Commons file Air composition pie chartJPG (greenhouse effect), and reducing temperature extremes between day and night (the diurnal temperature variation) The common name given to the atmospheric gases used in breathing and
Global GHG emissions from energy use and production far outweigh emissions from other activities The industrial processes, agriculture, landuse change and forestry, and waste management sectors together account for 37 percent of all global GHG emissions in the accompanying pie chartTrends in global GHG emissions • Global greenhouse gas emissions show no signs of peaking • Global CO 2 emissions from energy and industry increased in 17, following a threeyear period of stabilization • Total annual greenhouse gases emissions, including from landuse change, reached a record high of 535 GtCO 2e in All of the World's Greenhouse Gas Emissions in One Awesome Interactive Pie Chart By Margaret Badore Senior Editor Columbia
This pie chart illustrates how the various components of livestock production contribute to global GHG emissions Credit Tackling climate change through livestock – A global assessment of emissions and mitigation opportunities By (Gerber et al, 13) The emissions profile for livestock production varies by speciesYou are About to View Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Emissions Data from Large Facilities Important Information about this Data Set This data set does not reflect total US GHG emissions The data was reported to EPA by facilities as of EPA continues to quality assure data and plans to release updated data periodicallyFood production is responsible for 26% of global greenhouse gas emissions;



Ww3 Arb Ca Gov Cc Inventory Pubs Reports 00 16 Ghg Inventory Trends 00 16 Pdf




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa
Energy, Fuel Economy & Emissions Caterpillar shares the concerns of governments and the public about the risks of climate change and supports global efforts to mitigate its impact We are committed to contributing to a reducedcarbon future We demonstrate this in many ways including through our significant progress in reducing greenhouse gas Chart of the day These countries create most of the world's CO2 emissions With CO2 levels on the rise, being able to track global emissions is crucial Just two countries, China and the US, are responsible for more than 40% of the world's CO2 emissions With CO2 levels still on the rise, being able to track the global emissions hotspotsLearn more about the major greenhouse gases by selecting pieces of the pie chart below Water Vapor It's a Gas!




Pin By Amanda Joy Ravenhill On Project Drawdown Ghg Emissions Global Warming Greenhouse Gas Emissions




Windsor S Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Global CO2 emissions declined by 58% in , or almost 2 Gt CO2 – the largest ever decline and almost five times greater than the 09 decline that followed the global financial crisis In 21 global energyrelated CO2 emissions are projected to rebound and grow by 48% as demand for coal, oil and gas rebounds with the economy The chart above and table below both show data compiled by the International Energy Agency, which estimates carbon dioxide (CO 2) emissions from the combustion of coal, natural gas, oil, and other fuels, including industrial waste and nonrenewable municipal waste Here we rank the top highest emitters of annual carbon dioxide in 18 (the most recentThat's one reason why climate change requires global action The graph below shows how the world's total greenhouse gas emissions are continuing to increase every year
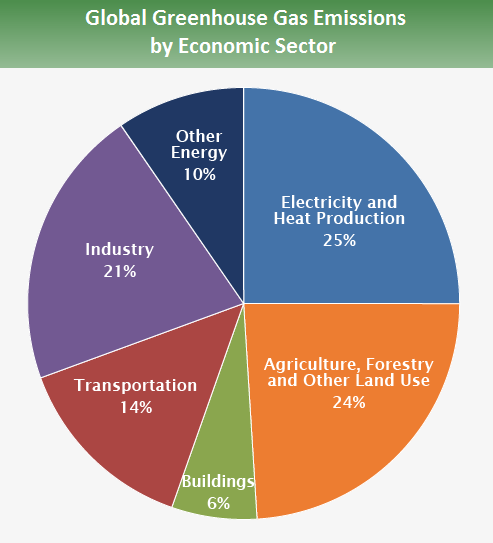



Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Data Us Epa




Ghg Emissions Manitoba Climate Change Connection
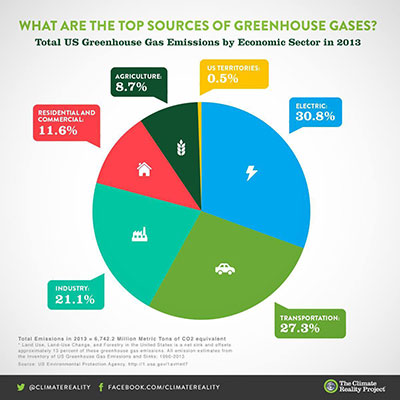
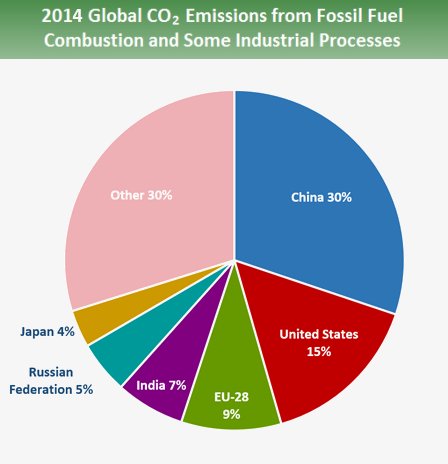
Globally, the primary sources of greenhouse gas emissions are electricity and heat (31%), agriculture (11%), transportation (15%), forestry (6%) and manufacturing (12%) Energy production of all types accounts for 72 percent of all emissionsThe next image shows CO 2 emissions from fossil fuel combustion by country In 15, China's share was 28 percent of the world's CO 2, while the US share was 15 percentThe next closest country, India, emitted about 6 percent of the CO 2Clearly, to bring down global emissions from the energy sector, China and the US must lead the wayCarbon dioxide (CO 2) is the primary greenhouse gas emitted through human activitiesIn 19, CO 2 accounted for about 80 percent of all US greenhouse gas emissions from human activities Carbon dioxide is naturally present in the atmosphere as part of the Earth's carbon cycle (the natural circulation of carbon among the atmosphere, oceans, soil, plants, and animals)



1




Why Are High Emission Countries Lagging On Climate Protection Environment All Topics From Climate Change To Conservation Dw 12 12 19
And food waste is responsible for 24% of that figure Therefore food waste as a share of global emissions is 24% * 26 = 6% Latest data from the World Resource Institute's CAIT Climate Data Explorer reports that aviation accounts for 19% of global greenhouse gas emissions Food losses and waste The transportation sector is one of the largest contributors to anthropogenic US greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions According to the Inventory of US Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Sinks 1990–19 (the national inventory that the US prepares annually under the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change), transportation accounted for the largestHuman emissions of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases – are a primary driver of climate change – and present one of the world's most pressing challenges 1 This link between global temperatures and greenhouse gas concentrations – especially CO 2 – has been true throughout Earth's history 2 To set the scene, let's look at how the planet has warmed




A Pie Chart Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions




Livestock And The Environment Faqs Unl Beef
Global energyrelated CO2 emissions by sector Chart and data by the International Energy AgencyEmissions Gap Report 19 As the world strives to cut greenhouse gas emissions and limit climate change, it is crucial to track progress towards globally agreed climate goals For a decade, UNEP's Emissions Gap Report has compared where greenhouse gas emissions are heading against where they need to be, and highlighted the best ways to close 19 UK greenhouse gas emissions final figures xlsx and ods data tables updated New annex added final emissions by end user and fuel type 2 February 21
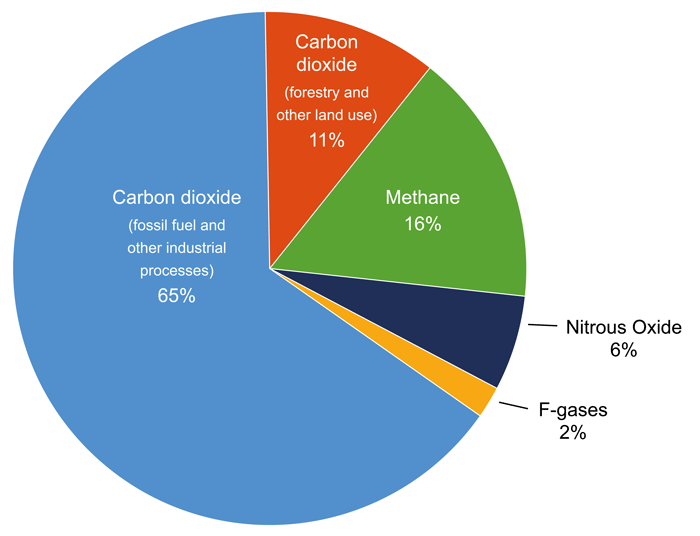



Causes Of Climate Change And Sea Level Rise Coastadapt




Greenhouse Gas Emissions
In 18 New Zealand's gross greenhouse gas emissions were 7 million tonnes of CO 2 e, 240 percent higher than 1990 and 10 percent lower than 17 In 18 Gross GHG emissions were mainly made up of carbon dioxide (445 percent), methane (435 percent), and nitrous oxide (96 percent) Carbon dioxide emissions were mainly produced by transport (470In 19, direct industrial greenhouse gas emissions accounted for 23 percent of total US greenhouse gas emissions, making it the third largest contributor to US greenhouse gas emissions, after the Transportation and Electricity sectors Including both direct emissions and indirect emissions associated with electricity use, industry's share of total US greenhouse gas emissions in 19 was 30 percent, making it the largest contributor of greenhouse gases The European Union remains a global leader in reducing greenhouse gas emissions The European Commission has proposed a significant cut in emissions by 30 and net zero emissions by 50 Seven Charts on Climate Policies for Key Sectors in the European Union




Colorado S Greenhouse Gas Reduction Roadmap Raises Concerns




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa
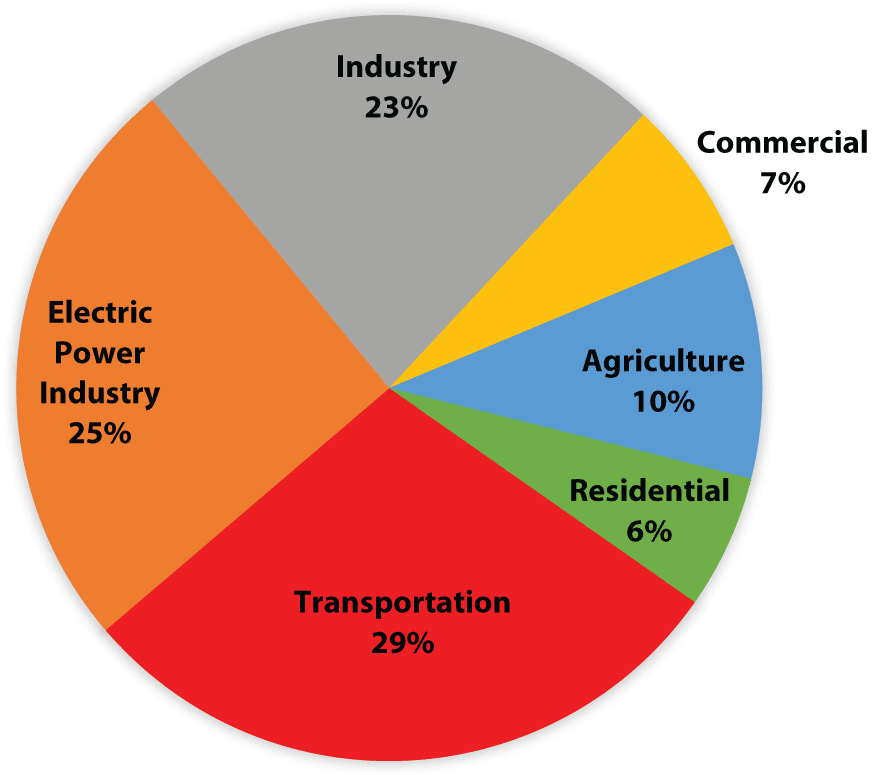
The gap between the promise of energy for all and the fact that almost one billion people still do not have access to electricity The gap between the latest scientific evidence highlighting the need for evermore rapid cuts in global greenhouse gas emissions and the data showing that energyrelated emissions hit another historic high in 18 To prevent the worst effects of climate change, we need to get to zero net greenhouse gas emissions in every sector of the economy within 50 years—and as the IPCC recently found, we need to be on a path to doing it in the next 10 years That means dealing with electricity, and the other 75% too Bill Gates 275M subscribers The pie chart above illustrates the 18 US humancreated greenhouse gas emissions and does not include natural sources and sinks of greenhouse gases Fluorinated gases, methane, and nitrous oxide have a large impact on global warming despite being a small percentage of emitted greenhouse gases




The Pie Chart Of The Main Elements 4 Of A Person S Carbon Footprint Download Scientific Diagram




Chart Of The Day Greenhouse Gas Pollution In California Streets Mn
Under the UN Kyoto Protocol, many industrialized nations around the world agreed to reduce their collective greenhouse gas emissions by about 5 percent of their 1990 amounts by 12 Although the goals of this agreement have not been met, the year 1990 remains an important point of reference for efforts to limit greenhouse gas emissionsIndia (see Greenhouse gas emissions by India) 3347 2870 2217 Russia (see Greenhouse gas emissions by Russia) 1630 1992 2670 1381 Japan 1231 1155 1310 1411 Brazil 1421 1050 524 Germany 1 777 918 7 Indonesia 1704 506 Canada (see Greenhouse gas emissions by Canada) 716 763 575 Mexico 695 718 528 Iran 8 876 572 South Korea 673 732However, these data are available mainly for a group of mostly developed countries that account for only about half of global greenhouse gas emissions




Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Gas 14 U S Environmental Download Scientific Diagram




Breakdown Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions France 17 Statista
Despite a dip in greenhouse gas emissions from the COVID19 economic slowdown, the world is still heading for a catastrophic temperature rise above 3°C this century – far beyond the goals of the Paris Agreement But UNEP's Emissions Gap points to hope in a green pandemic recovery and growing commitments to netzero emissions The accompanying charts show greenhouse gases by gas and source The burning of fossil fuels is the biggest culprit and much is being done to reduce it as a percentage of overall energy supply the adoption of solar, wind , geothermal , hydroelectric and others will go a long way toward reigning in this piece of the pie US CO2 emissions from petroleum and other liquids declined by 08% ( MMmt) in 19 compared with 18 With increased consumption, US natural gas CO2 emissions increased in total 356% (443 MMmt) from 07 to 19 From 18 to 19, natural gasrelated CO2 emissions increased by 33% (54 MMmt)
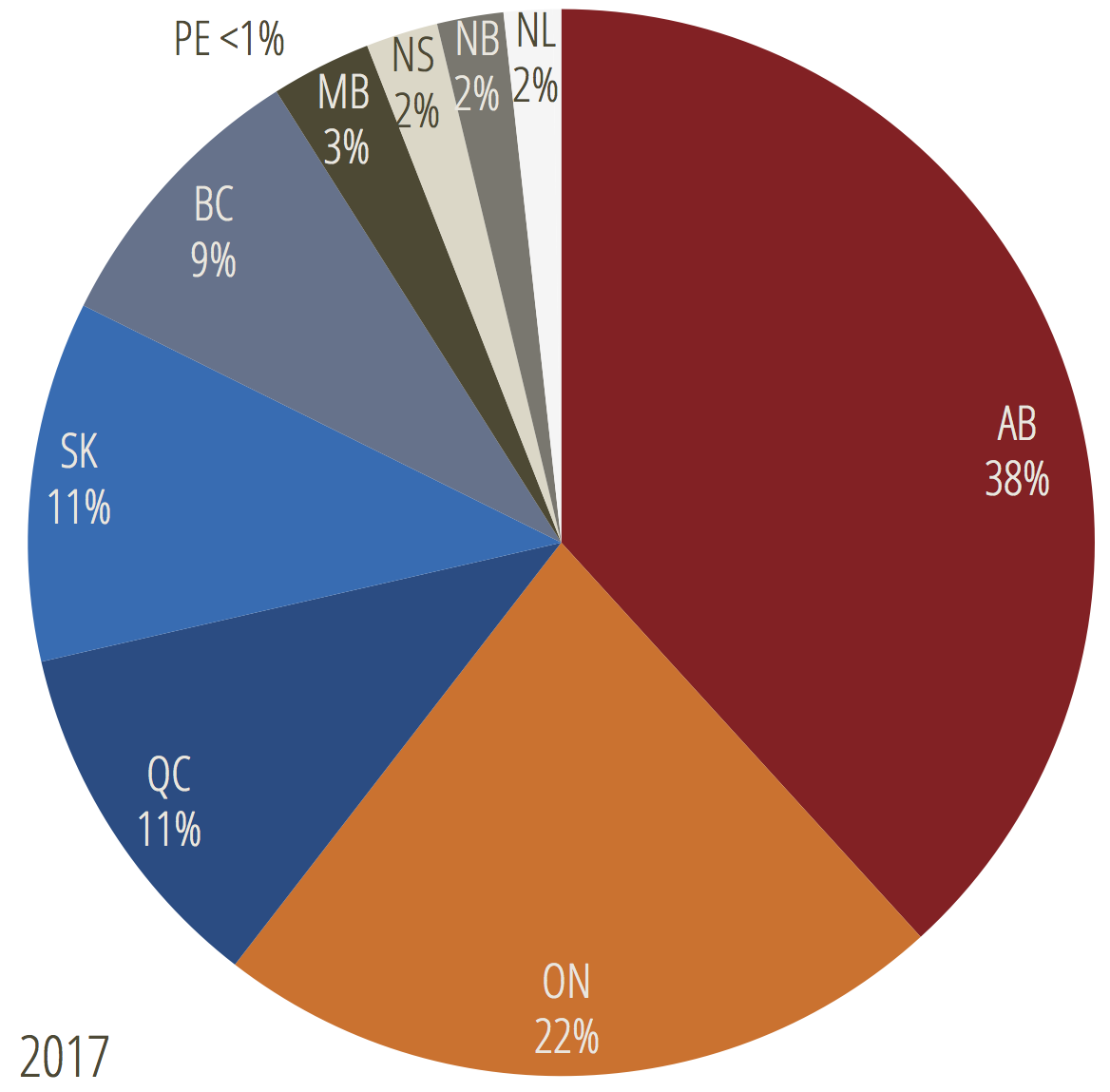



The Most Important Climate Numbers You Need To Know Blog Posts Pembina Institute




Climate Change And Zero Waste Eco Cycle Solutions Hub
The Global greenhouse gas emissions indicator reports global human emissions of greenhouse gases (GHGs) for 05 and 18 Emissions from energy and nonenergy related sources are included in this indicator, while emissions from land use, land use change and forestry are excluded The emissions of GHGs include carbon dioxide, methane, nitrousThis feature will be available in the next phase X User Guidance for the NonCO 2 Greenhouse Gases Publication Tool A data exploration tool for viewing nonCO2 GHG projections and mitigation assessments as compiled in the EPA report, Global NonCO2 Greenhouse Gas Emission Projections & Mitigation 1550Global emissions in 16 (minus crossboundary emissions), as the sum of those in the chart, was approximately 34 to 35 billion tonnes of CO 2 Adding one billion individuals with a per capita footprint of 113 tCO 2 per person per year would equal an addition 11 billion tonnes of CO 2 per year (1 billion*113 = 113 billion tonnes) This is equivalent to almost onethird of global emissions




Report 5 How Do We Contribute Individually To Global Warming Hinkle Charitable Foundation
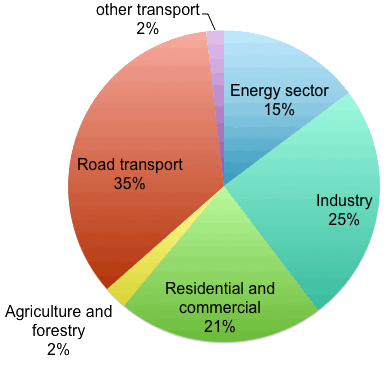



How Do Greenhouse Gas Emissions Presently Evolve Jean Marc Jancovici
Atmosphere of Earth Wikipedia The pie chart example "Atmosphere air composition" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Pie Charts solution of the Graphs and Charts area in ConceptDraw Solution Park Draw A Pie Chart To Represent The Gases That Contribute To Greenhouse Effect



How Do Greenhouse Gas Emissions Presently Evolve Jean Marc Jancovici



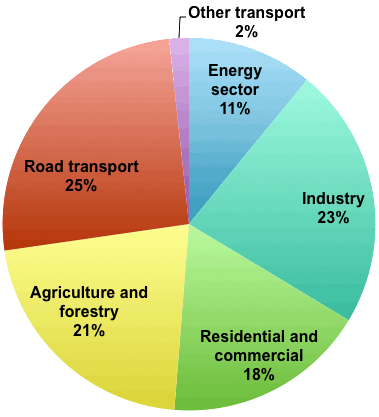
Agriculture Causes Less Emissions Than Transportation




Greenhouse Gas Emissions In Santa Fe City Of Santa Fe New Mexico



Agriculture And Greenhouse Gas Emissions G310 Mu Extension




Windsor S Greenhouse Gas Emissions



Livestock Emissions Geog 438w Human Dimensions Of Global Warming




How To Neutralise Your Greenhouse Gas Footprint



1
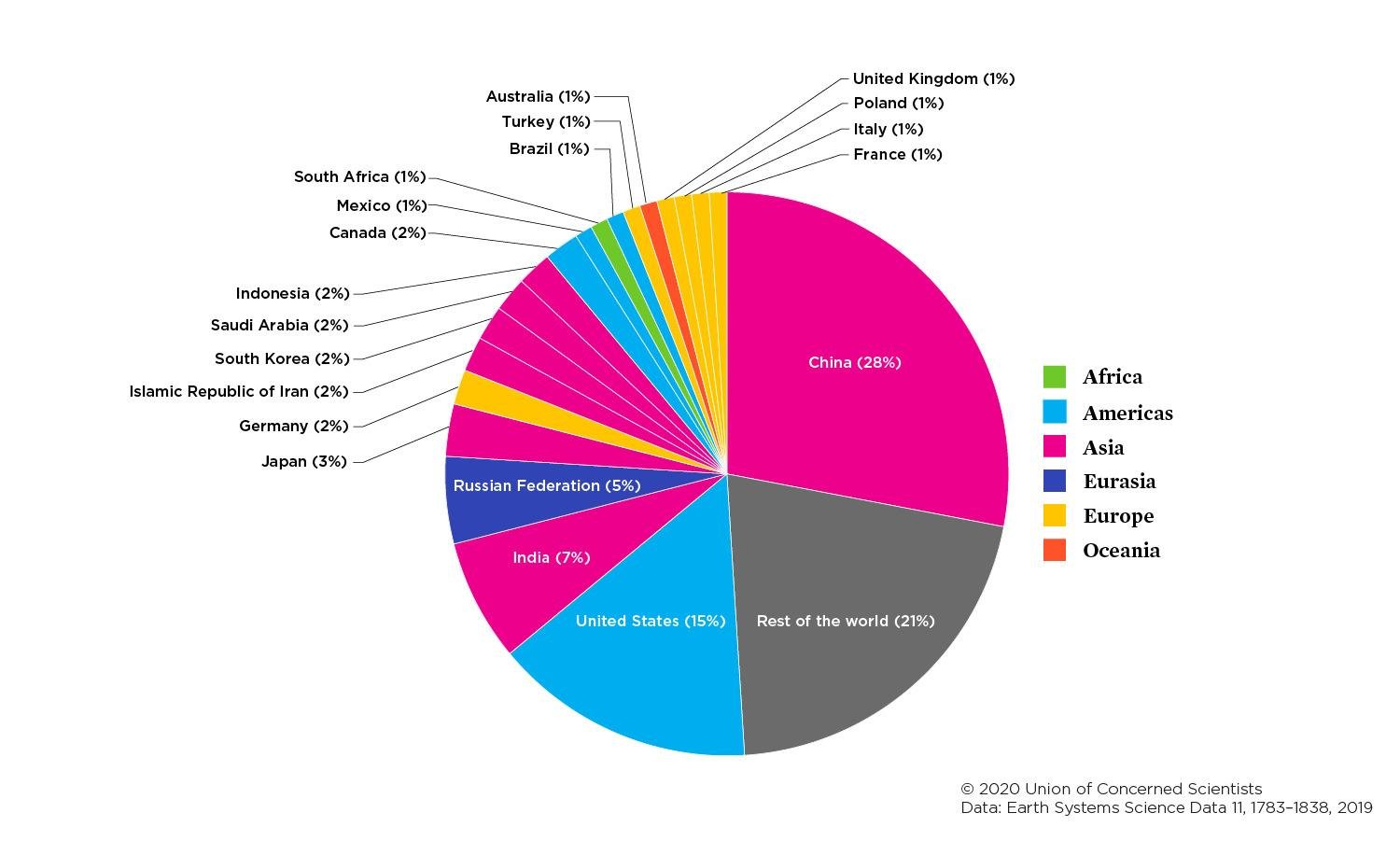



Each Country S Share Of Co2 Emissions Union Of Concerned Scientists



Record High For Global Carbon Emissions China Is The Leader Watts Up With That



Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Data Us Epa




These 10 Charts Will Show You The Danger Of Climate Change Emissions Greenhouse Gas Emissions Climate Change




Reducing Your Carbon Footprint Dwellsmart
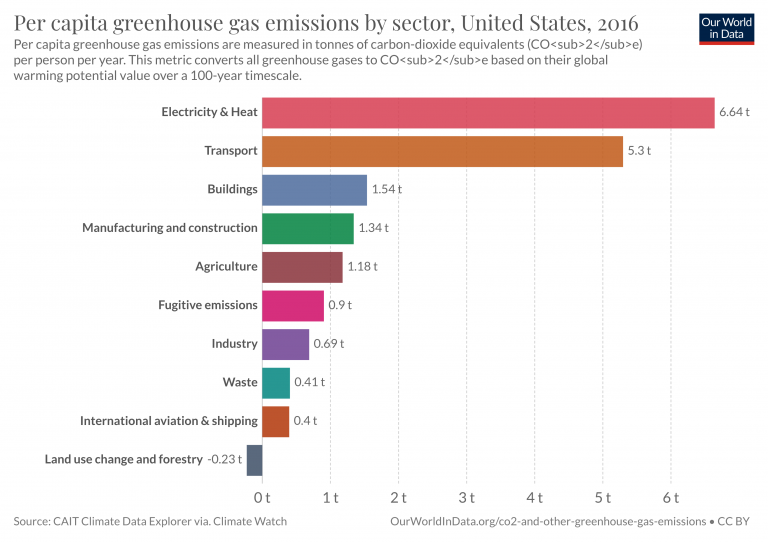



Emissions By Sector Our World In Data
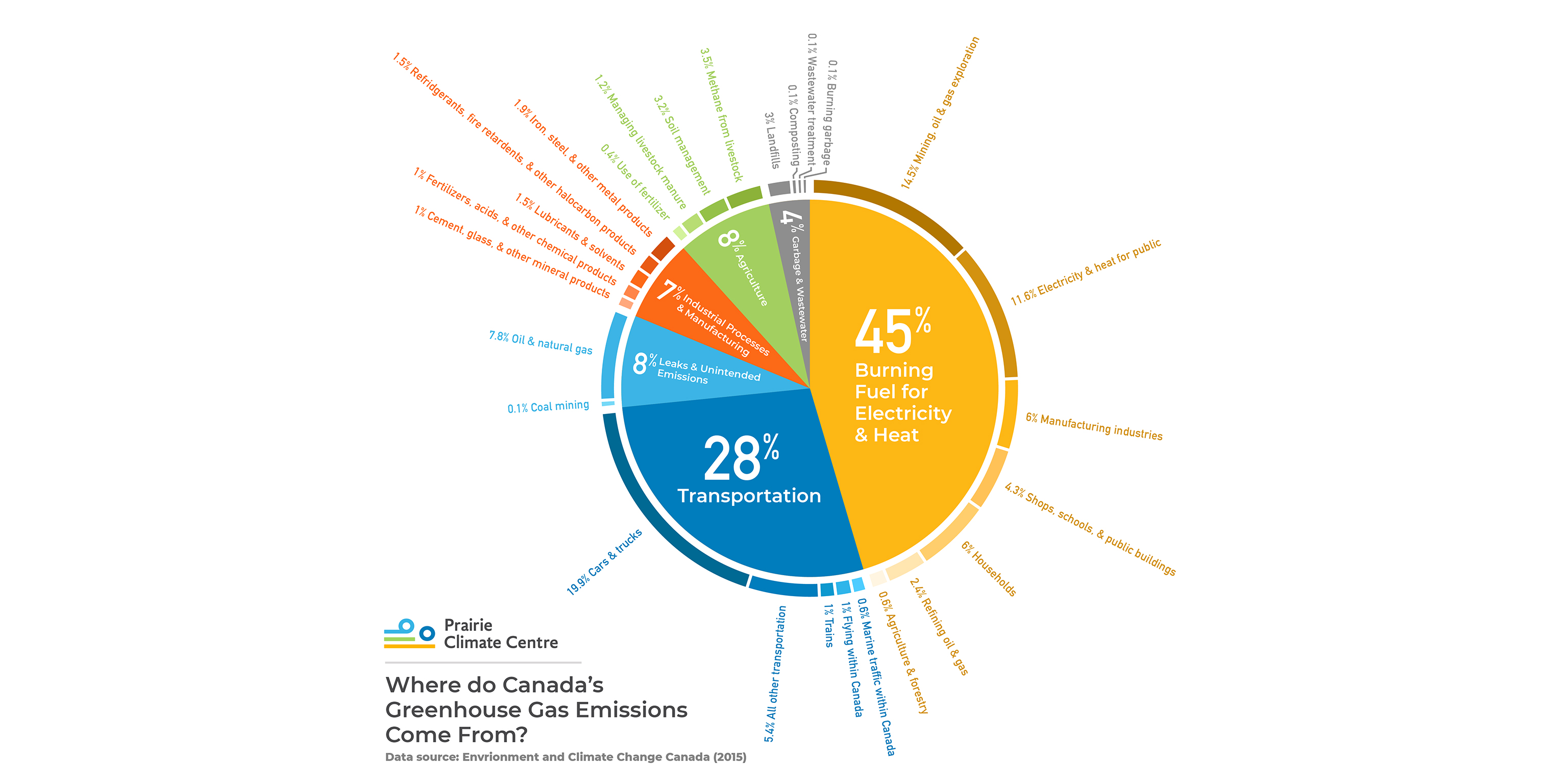



Where Do Canada S Greenhouse Gas Emissions Come From



Seattle S Carbon Footprint Assessing The Assessment Hugeasscity




Curbing Drilling On Federal Lands Won T Do Much For Climate



Emissions By Sector Our World In Data




Carbon Footprint Factsheet Center For Sustainable Systems



Emissions By Sector Our World In Data




Co2 Emissions From Commercial Aviation 18 International Council On Clean Transportation




Niwa Says Greenhouse Gas Methane Is On The Rise Again Niwa




Facing The Heat Man S Chilling Impact On Global Warming Nitty Gritty Stanford Magazine
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/16185122/gw_graphic_pie_chart_co2_emissions_by_country_2015.png)



Climate Change Animation Shows Us Leading The World In Carbon Emissions Vox




Emissions Of The Powerful Greenhouse Gas Sf6 Are Rising Rapidly World Economic Forum




Windsor S Greenhouse Gas Emissions
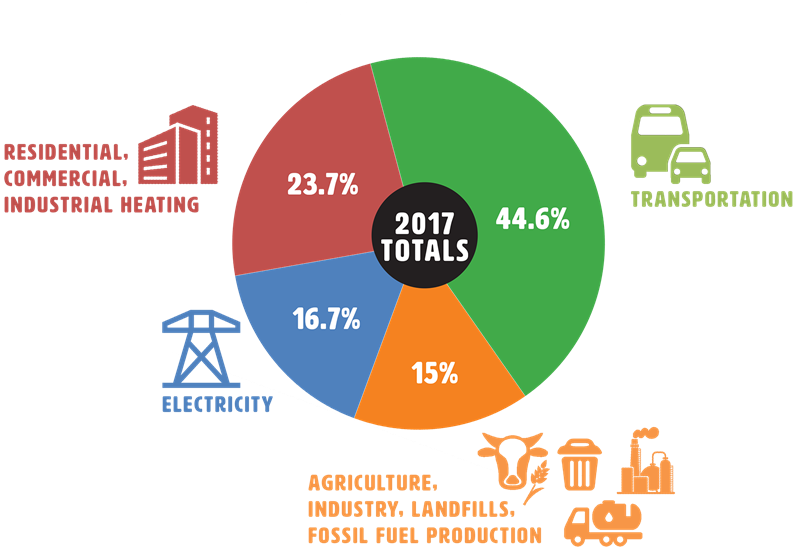



Kuow Sorry Climate Washington State S Carbon Emissions Stay Stubbornly High
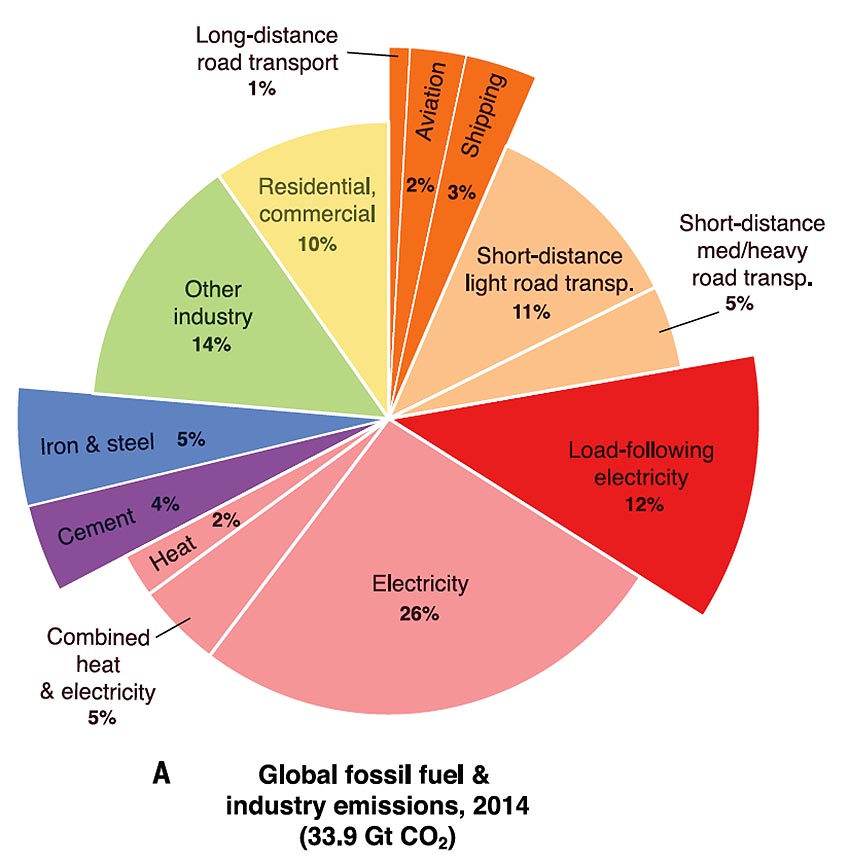



Researchers Envision Tomorrow S Net Zero Emission Energy Systems News Nrel
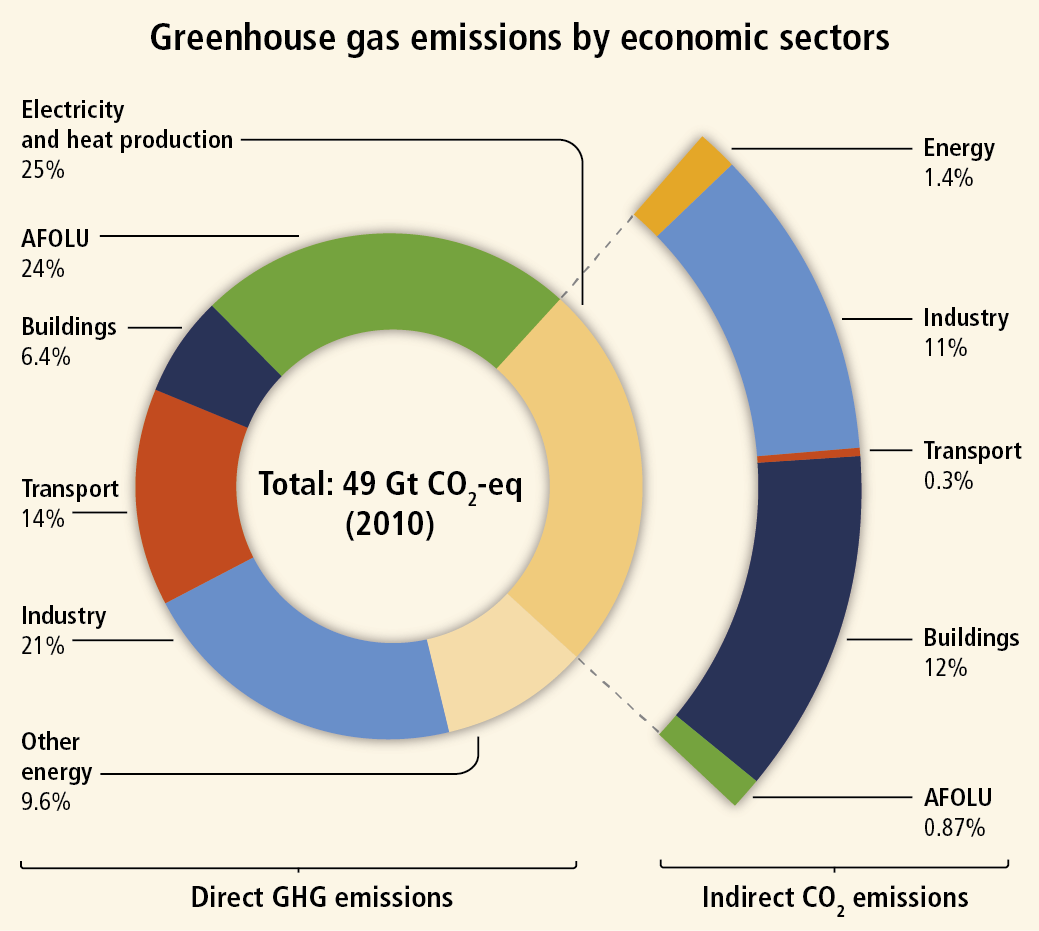



Impact Of Agriculture On Climate Change




Carbon Trading Cqr




Where Carbon Is Taxed Overview




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




Emissions Sustainability Umass Amherst
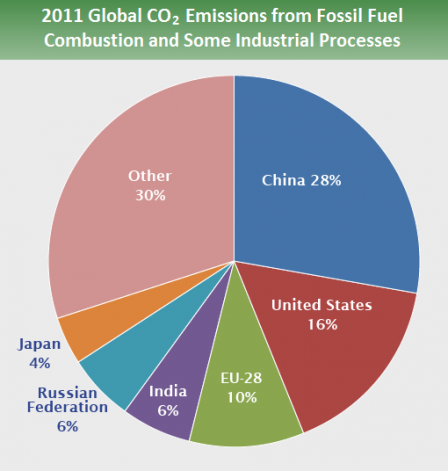



Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Data Greenhouse Gas Ghg Emissions Us Epa
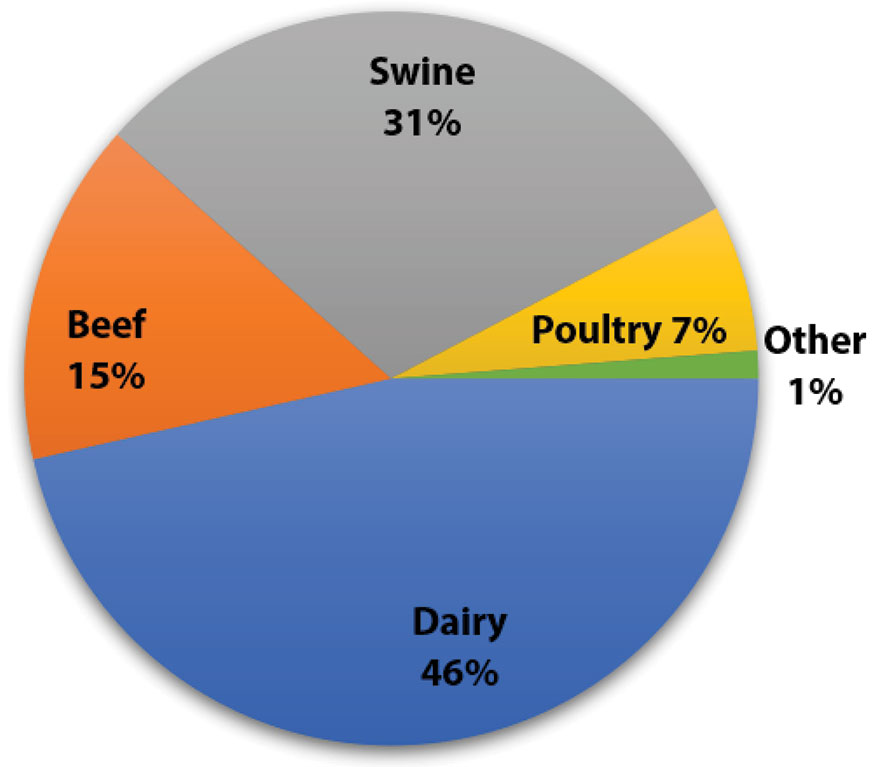



Agriculture And Greenhouse Gas Emissions G310 Mu Extension



Emissions By Sector Our World In Data




File Annual World Greenhouse Gas Emissions In 05 By Sector Svg Wikipedia




Global Warming Pie In The Sky




National Emissions Climate Energy And Society College Of Liberal Arts Auburn University




Global Gas Emissions Climate Energy And Society College Of Liberal Arts Auburn University
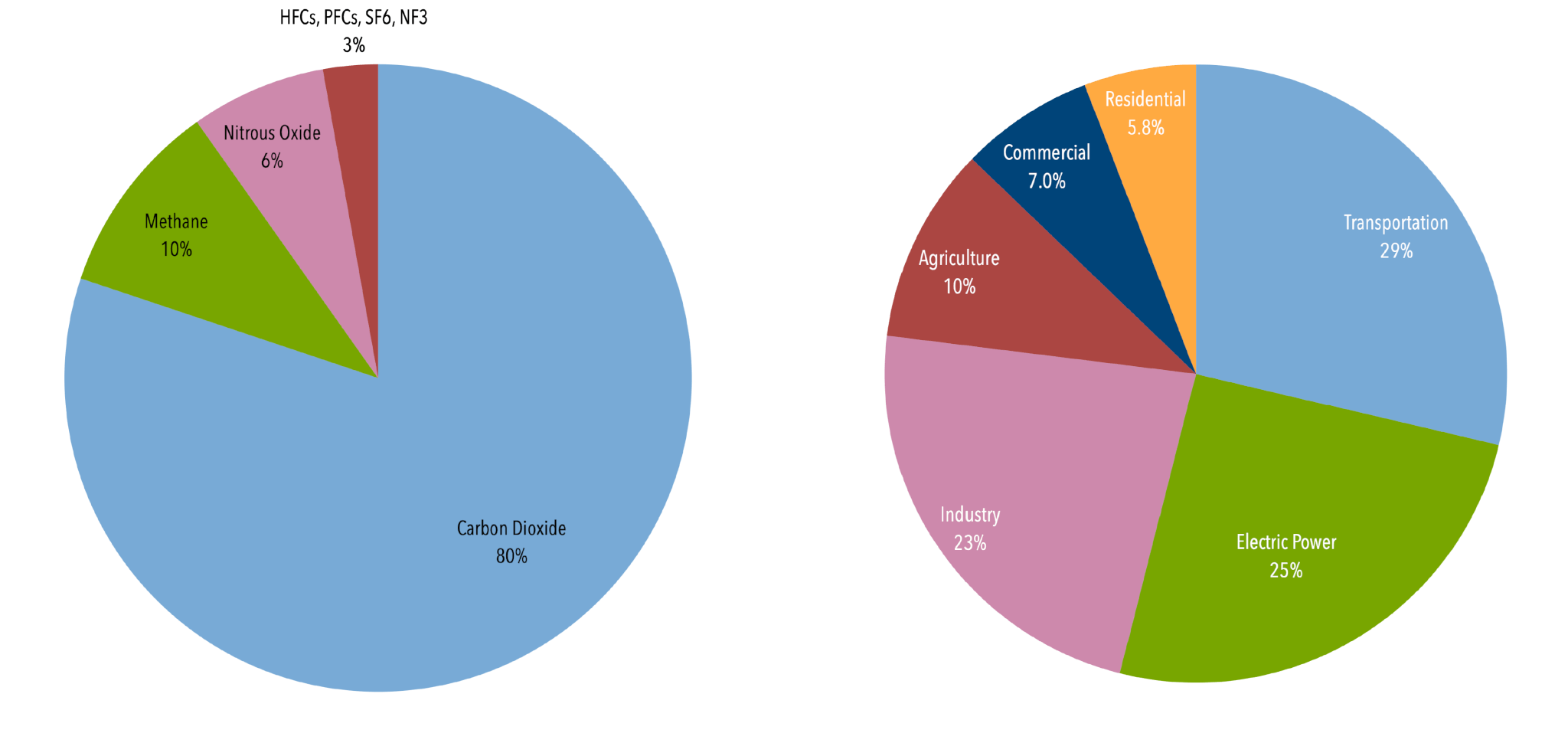



U S Emissions Center For Climate And Energy Solutions
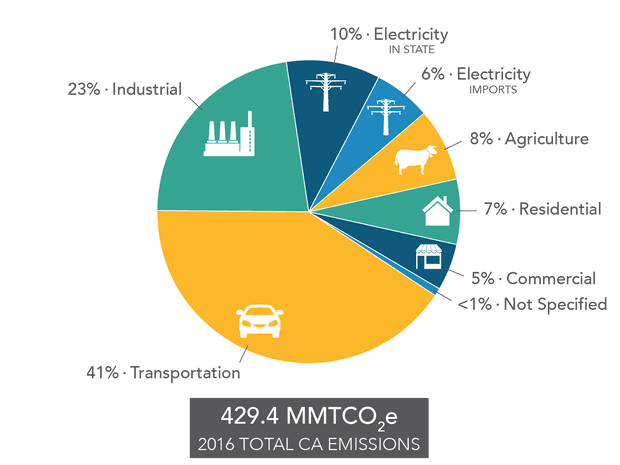



California Plans To Show The World How To Meet The Paris Climate Target
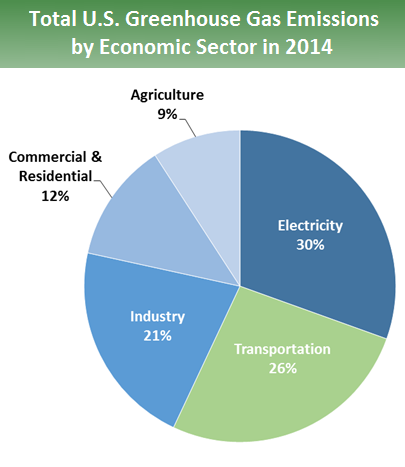



Sources Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions Greenhouse Gas Ghg Emissions Us Epa




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Inventory Cuyahoga County Planning Commission




Have A Spooky Halloween Baxt Ingui Architects P C
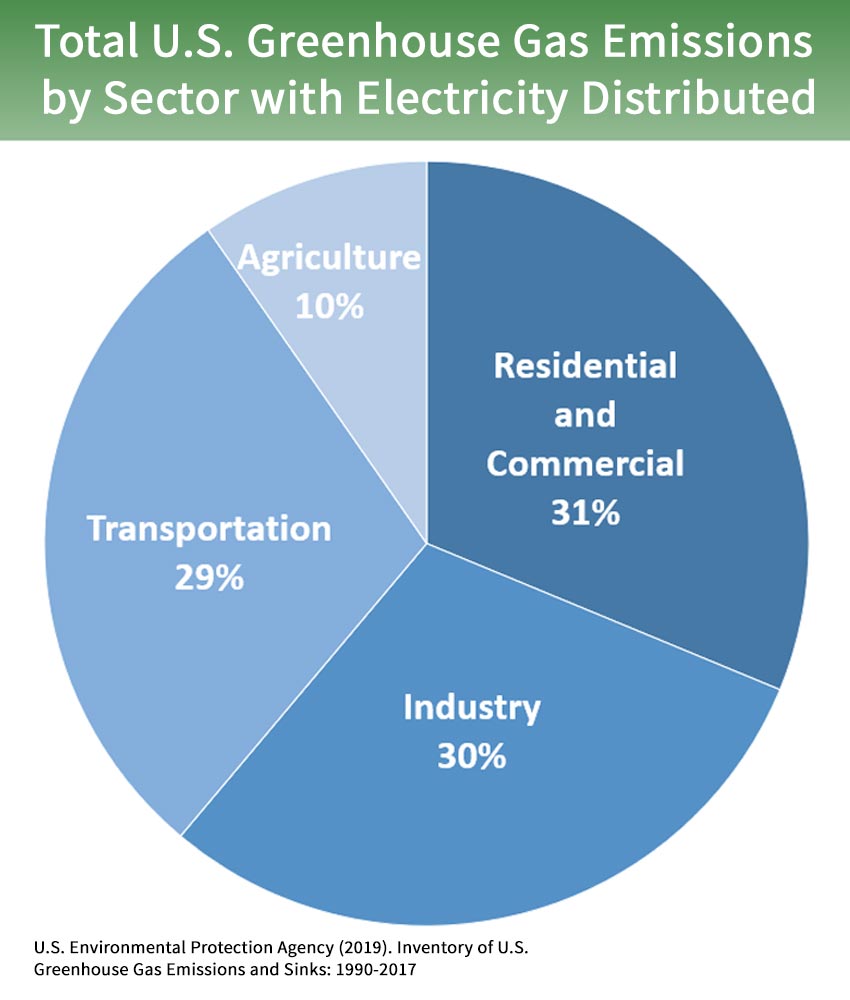



Us Transportation Emissions Geog 438w Human Dimensions Of Global Warming



3
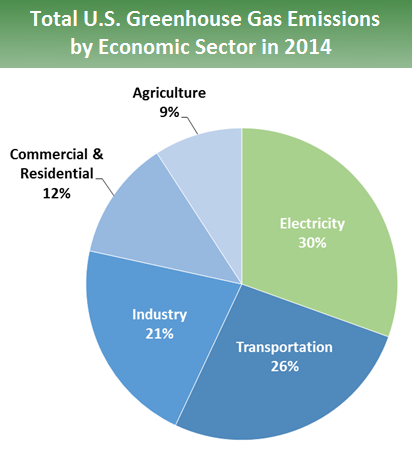



Sources Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions Greenhouse Gas Ghg Emissions Us Epa




Sources Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions Us Epa




The World Thorium Reserves Pie Chart Generated From Data On Mineral Download Scientific Diagram
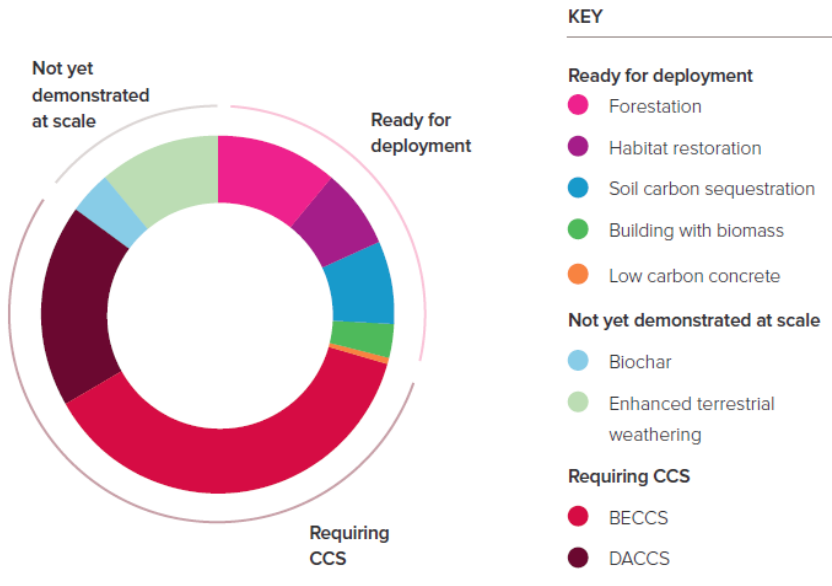



Uk Could Become Net Zero By 50 Using Negative Emissions
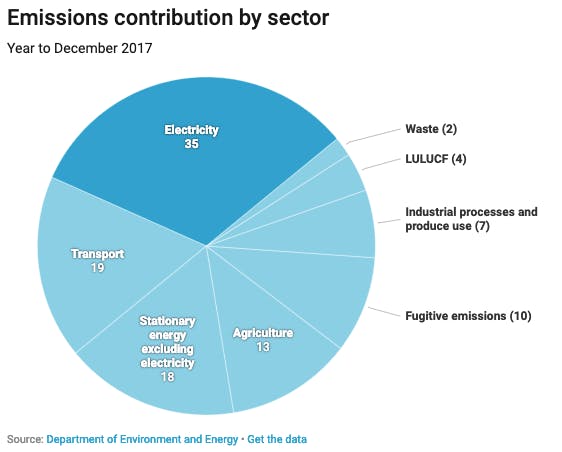



How To Neutralise Your Greenhouse Gas Footprint Opinion Eco Business Asia Pacific
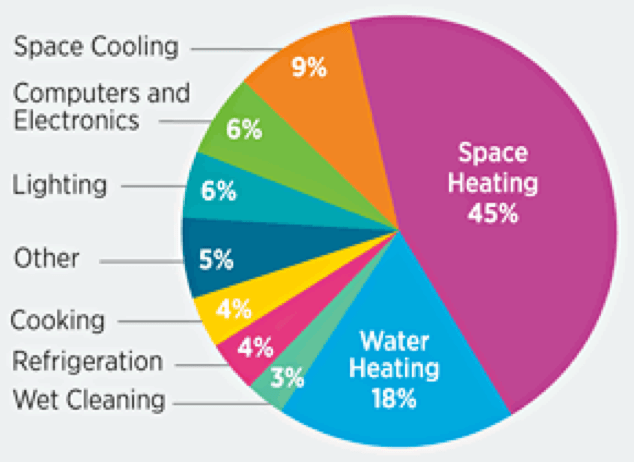



Carbon Dioxide Emissions And Carbon Footprint Mahb
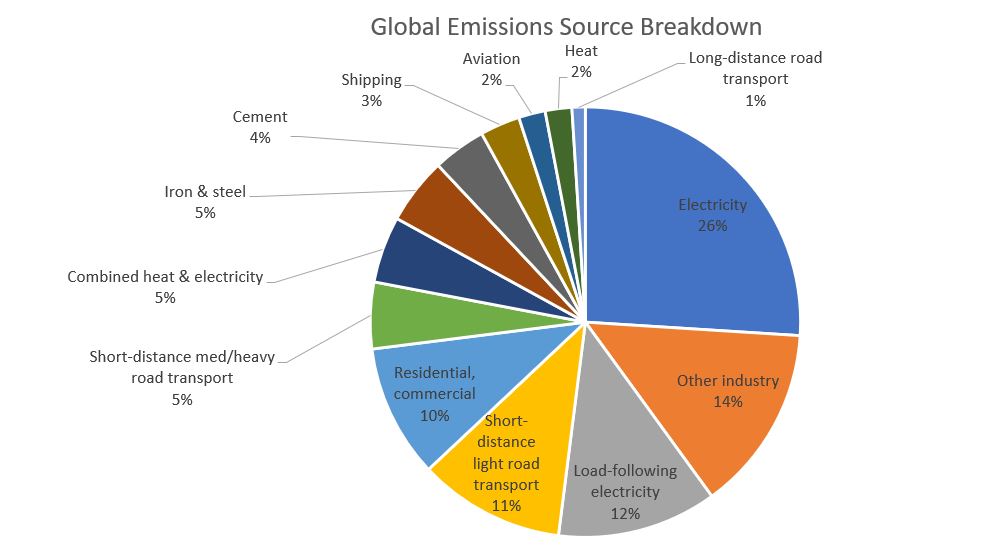



Carbonfootprint Com Climate Change
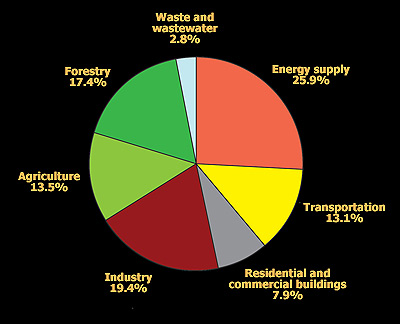



Tackling The Global Warming Challenge
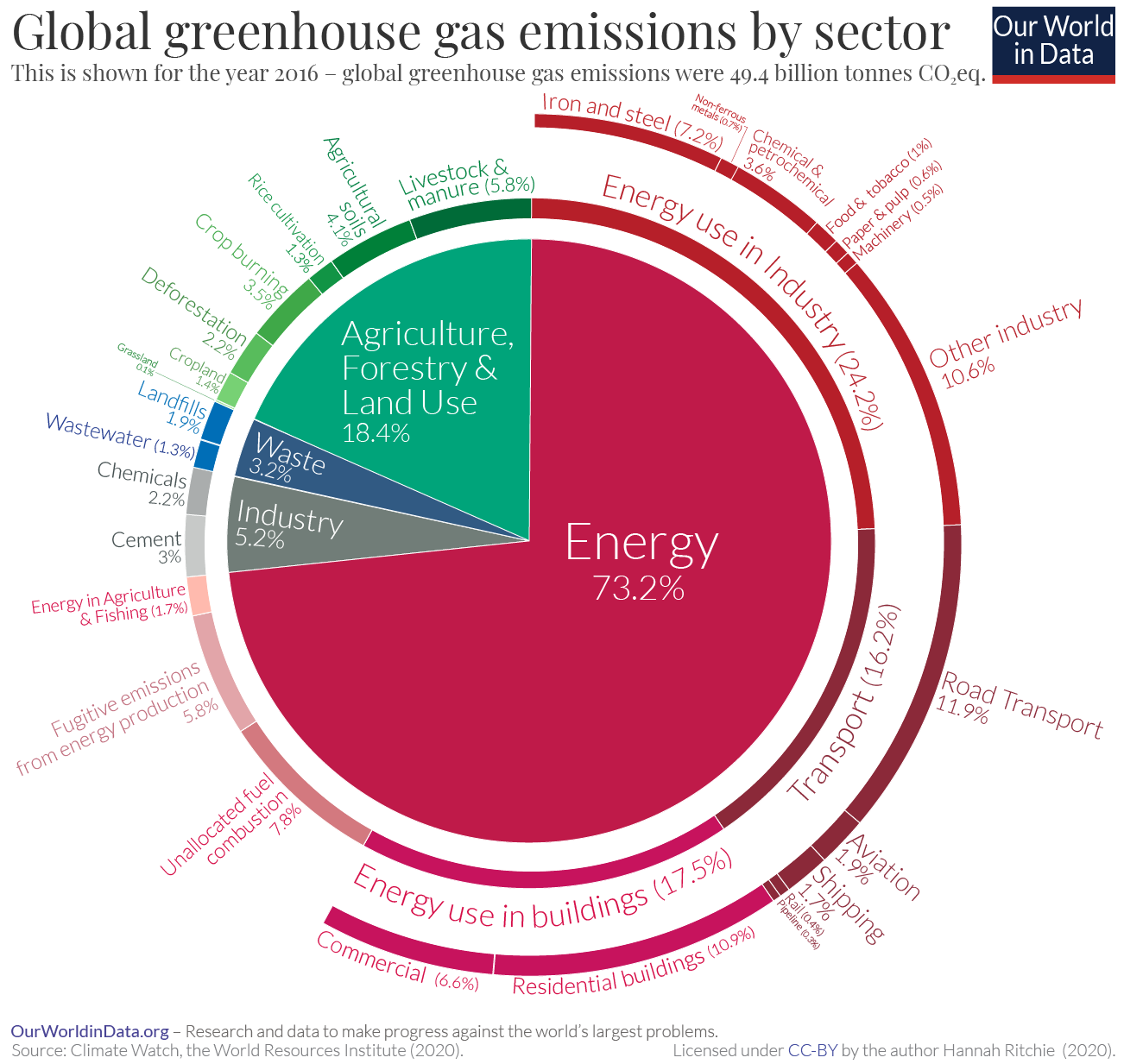



Sector By Sector Where Do Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Come From Our World In Data




Climate Greenhouse Gases Sustainability



Livestock Emissions Geog 438w Human Dimensions Of Global Warming




Chart Of The Day These Countries Have The Largest Carbon Footprints World Economic Forum
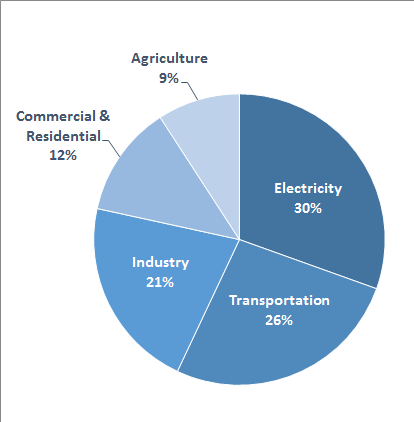



Methane Emissions Replace Co2 Emissions Is This Progress Planetizen News
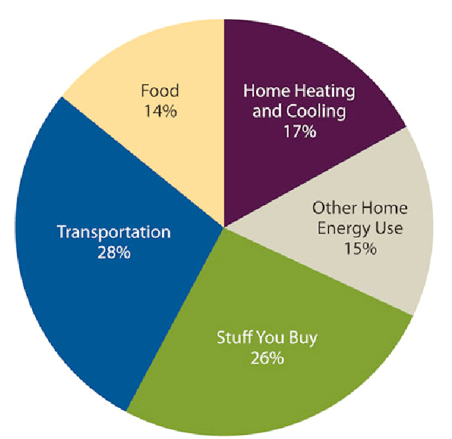



Carbon Dioxide Emissions And Carbon Footprint Mahb
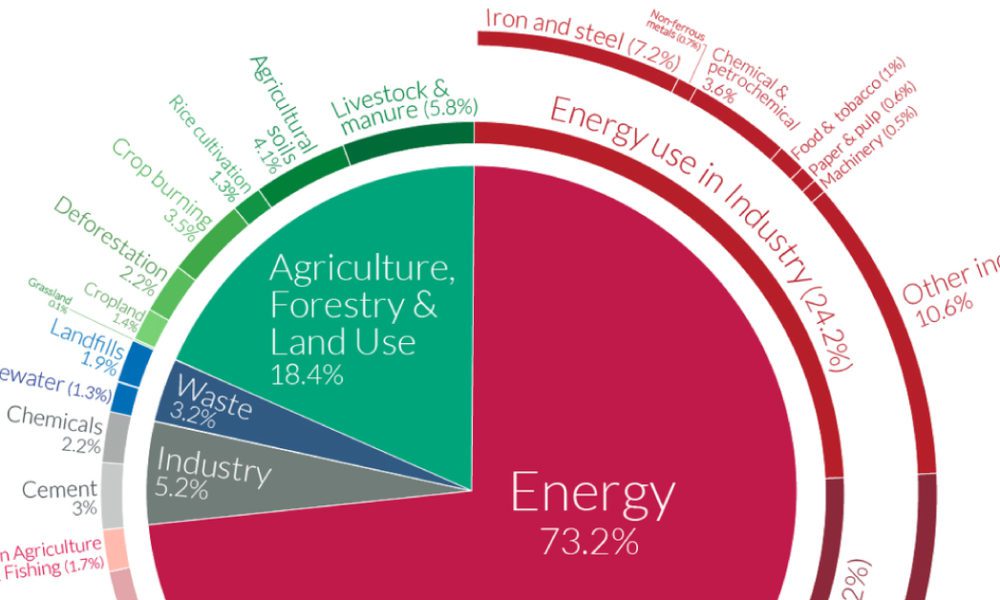



A Global Breakdown Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Sector




Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Data Us Epa




Canada Ghg By Province Climate Change Connection
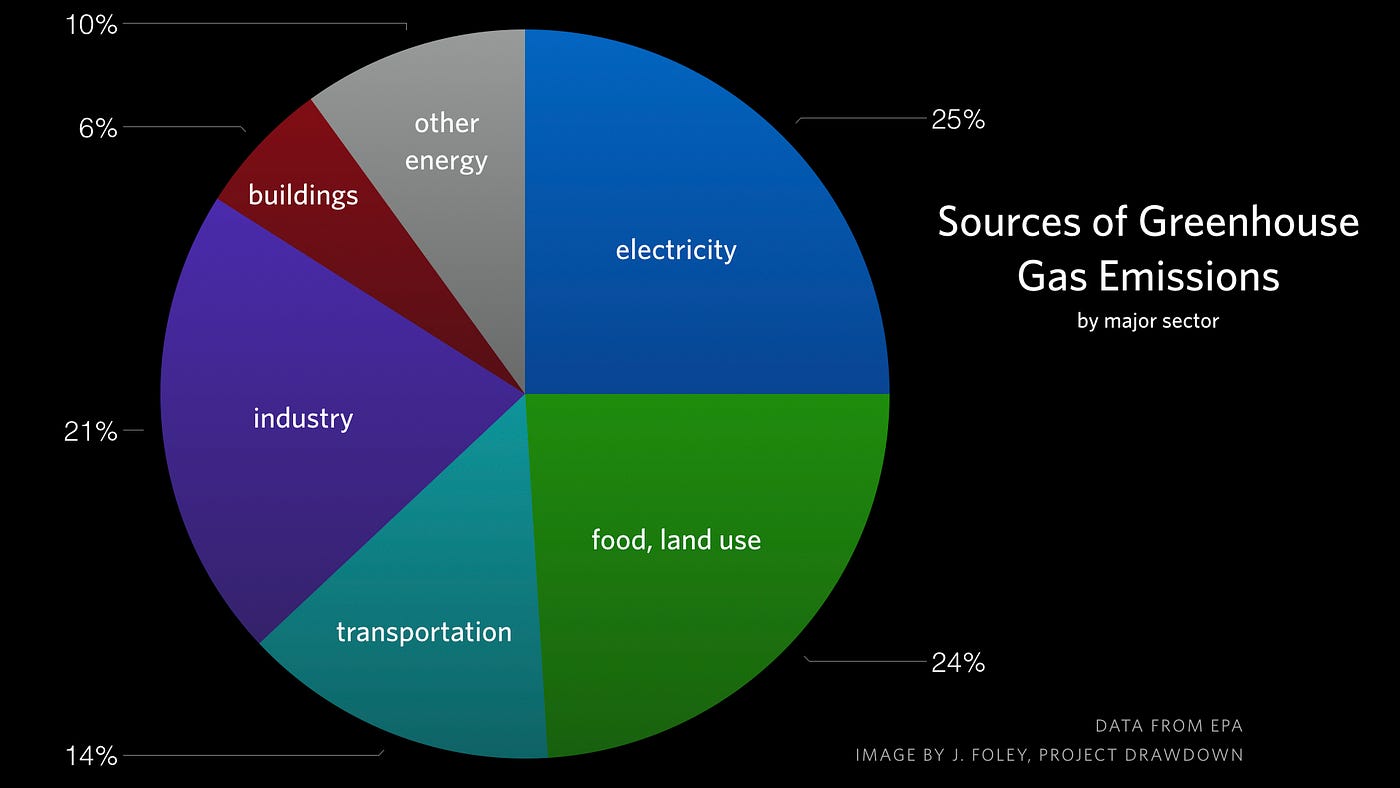



Major Causes Of Climate Change Globalecoguy Org



Truevaluemetrics Impact Accounting For The 21st Century
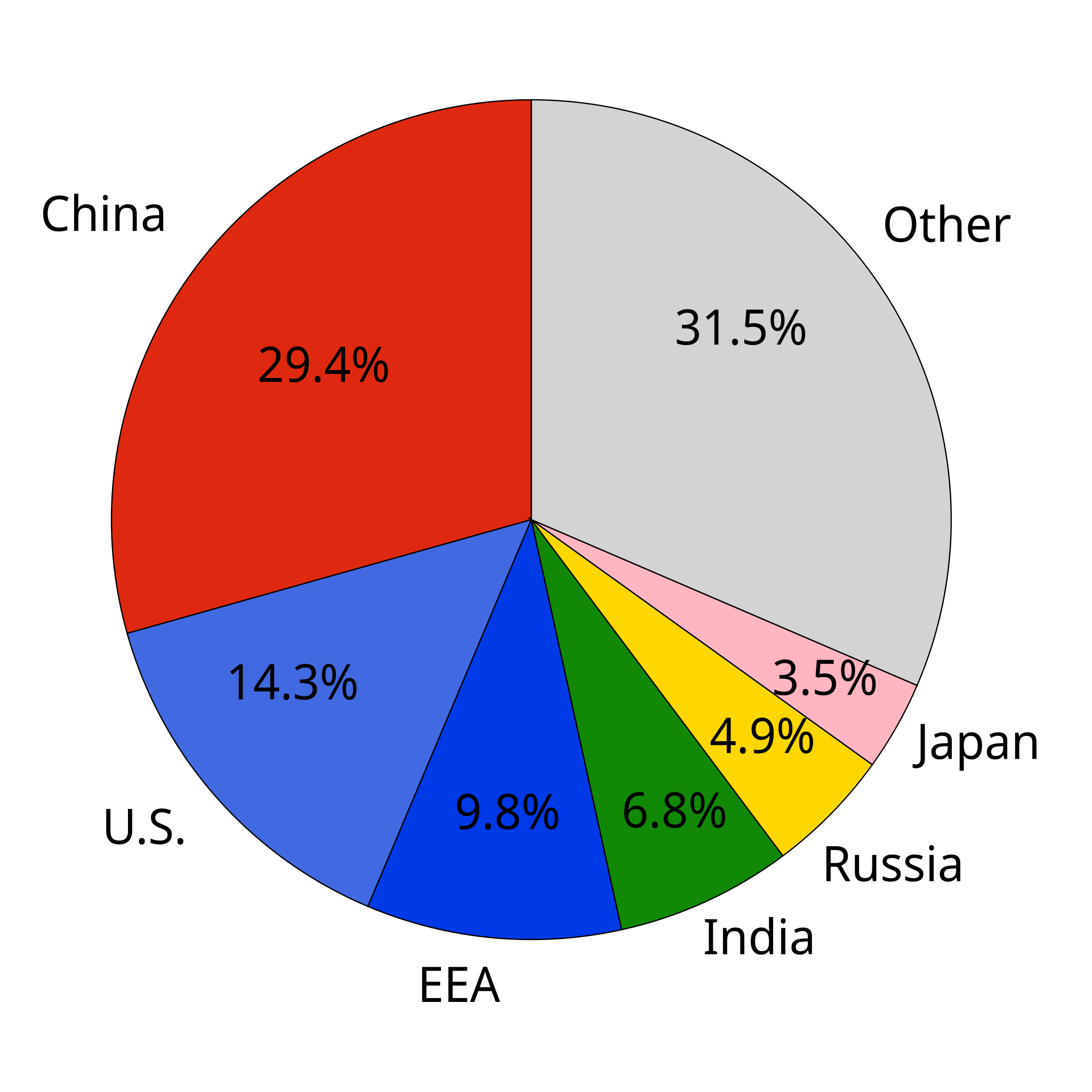



File Co2 Emission Pie Chart Svg Wikimedia Commons




How To Avoid A Climate Disaster Unsolicited Feedback




Dnr Reports 3 Increase In Iowa Greenhouse Gas Emissions Iowa Environmental Focus




Sources Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions Us Epa
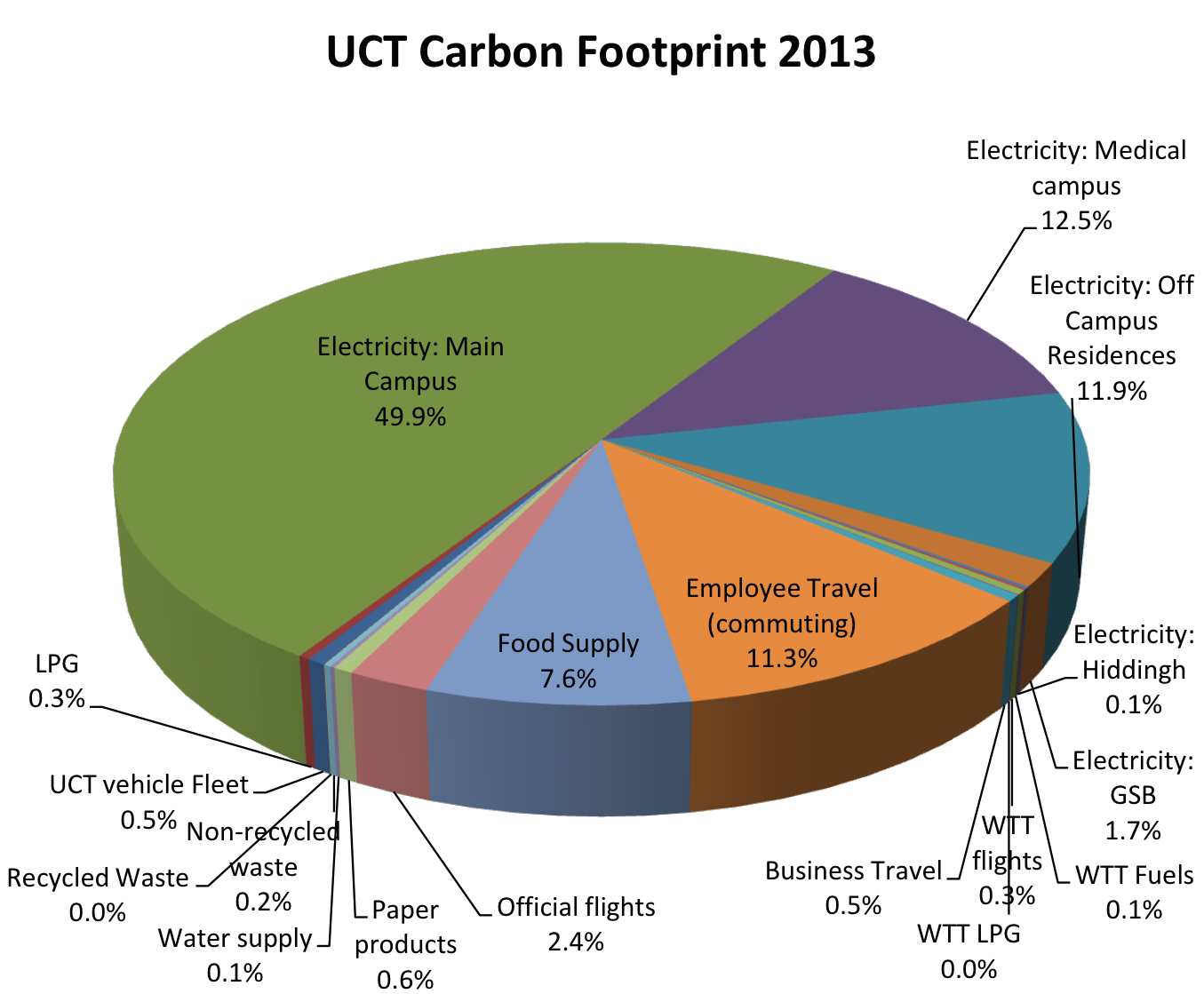



Uct Carbon Footprint




Chart Of The Day Greenhouse Gas Pollution In California Streets Mn



1
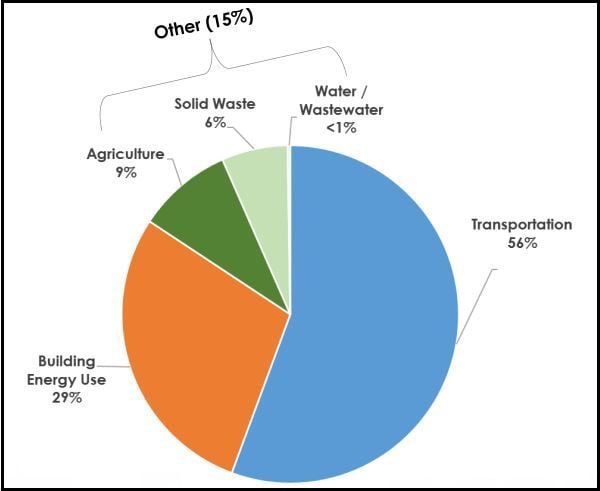



Santa Barbara County S Greenhouse Gas Emissions Going Up Not Down Local News Santamariatimes Com




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa



Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Country And Sector Used Cait As Data Source Climatechange
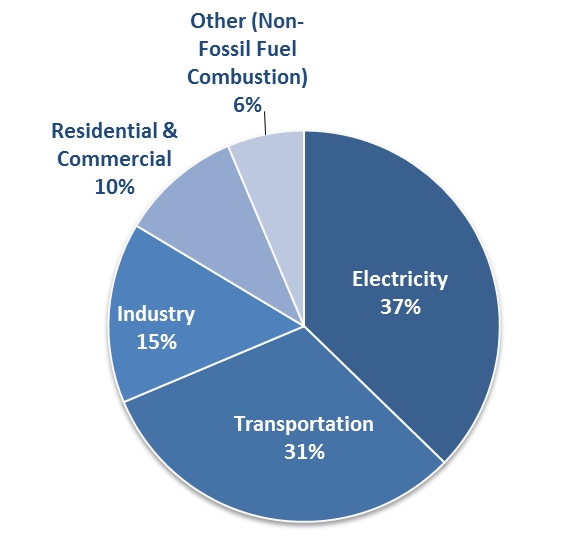



Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Matter Of Trust
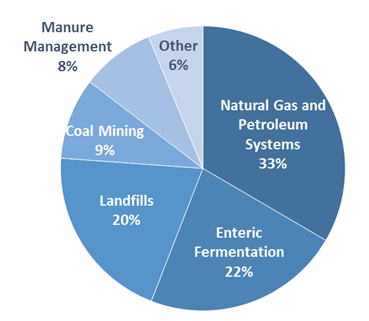



Methane Emissions Replace Co2 Emissions Is This Progress Planetizen News
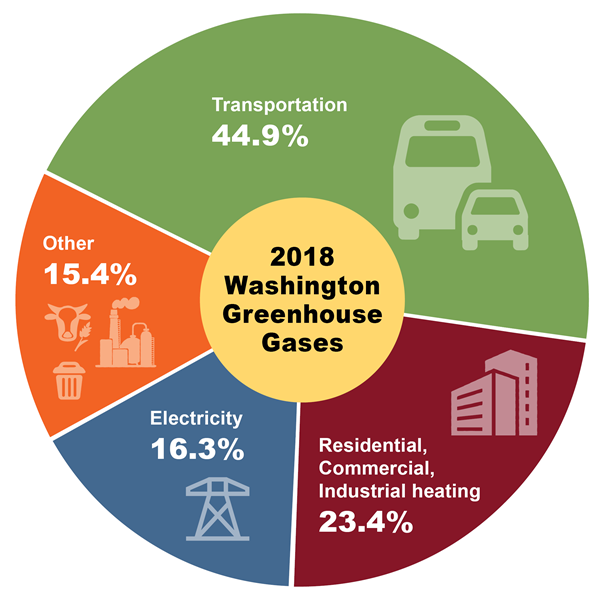



18 Data Washington State Department Of Ecology




Inventory Of U S Greenhouse Gas Emissions And Sinks 1990 11 Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse Gas Emissions Climate Change




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa



Carbon Footprint Factsheet Center For Sustainable Systems



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿